Skip to content
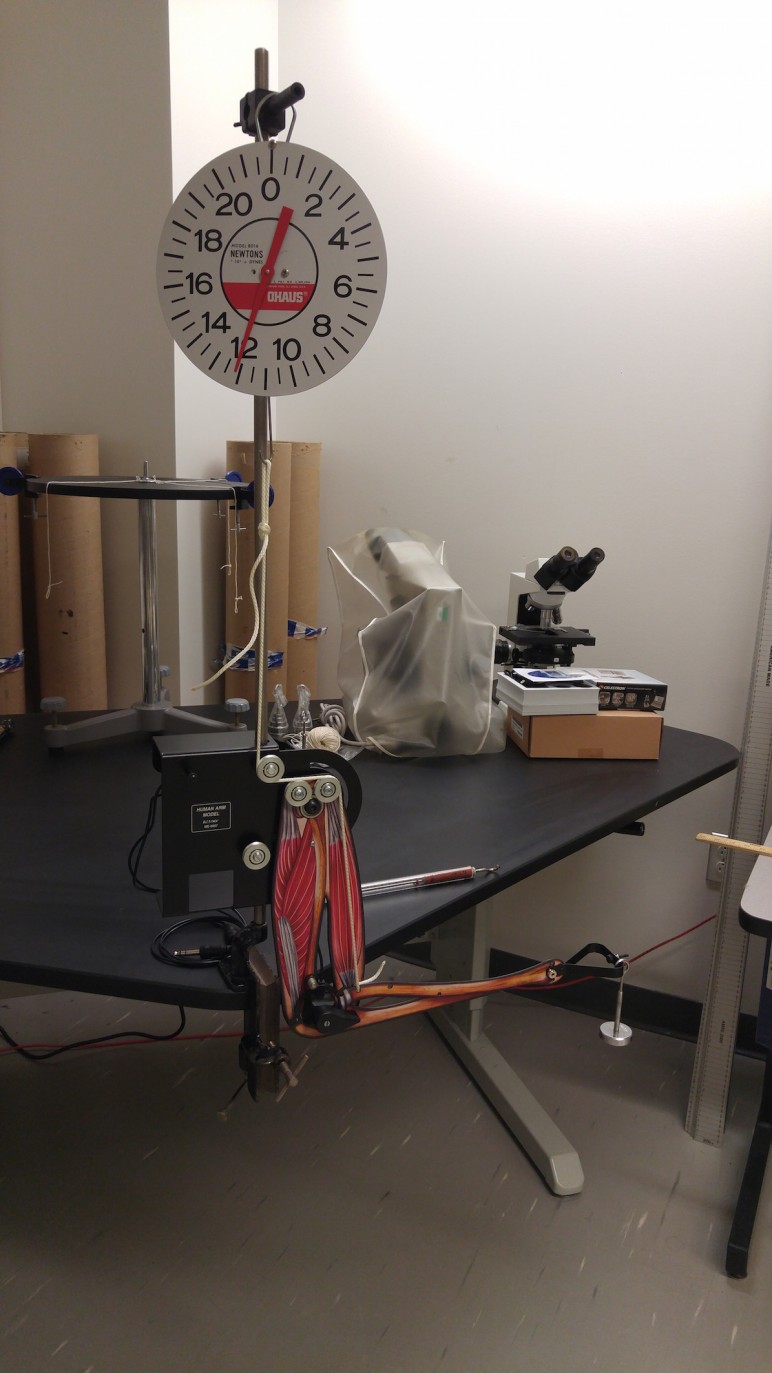



- Human arm model can be used to show how muscle tension in bicep (or tricep) relates to magnitude of force on hand, in various orientations.
- Picture above shows how 12 N of muscle tension are required to hold a mass weighing 1 N, in the hand, when the forearm is held at a 90 degree angle.
- Model allows for several different configurations and activities. See: https://www.pasco.com/prodCatalog/PS/PS-2611_human-arm-model/index.cfm
- Located in L02, section B4.
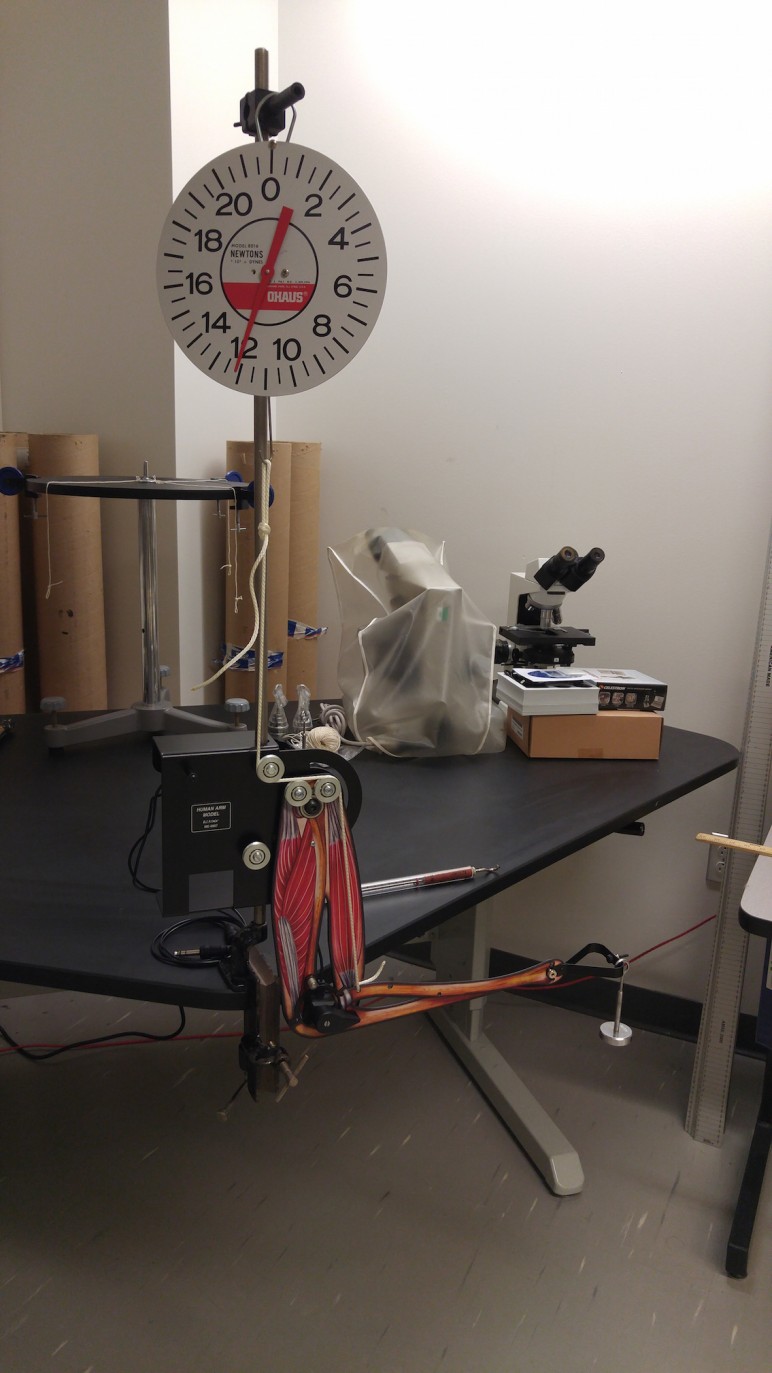


- This model can be used to demonstrate the amount of muscle tension required to hold the arm in various positions.
- The above picture shows that a 1 N weight, held in the hand with the forearm at a 90 degree angle, produces a bicep tension of 12 N.
- Model allows for several different configurations and activities. See: https://www.pasco.com/prodCatalog/PS/PS-2611_human-arm-model/index.cfm
- Located in L02, section B4.


- Build cubes, octahedrons, tetrahedrons and triangular prisms – then
dip them in soapy glycerin mixture to produce surfaces of minimum energy.
- Study surface tension and demonstrate light refraction.
- Soap film surface contained by three dimensional framework will
automatically arrange itself to have the smallest possible surface
area. Soap films can be used to give visual answers to complex mathematical problems.
- Located in L02, section D1. Soap solution located in L01,
section B5.






