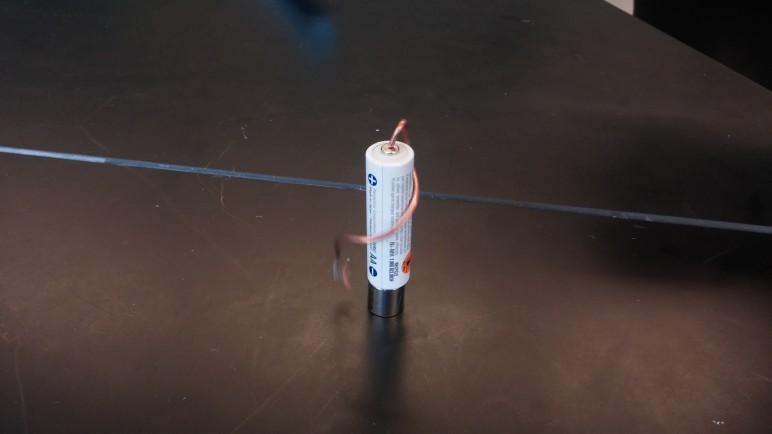
Wire balances on top of battery and is free to rotate. Top of wire touches positive terminal; bottom of wire touches magnet connected to negative terminal. Wire completes circuit and current travels through wire. Direction of magnetic field creates a Lorentz force that causes wire to turn.
Historical significance: First electric motor. First successful model devised by Michael Faraday. See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homopolar_motor
- Located in L01, section B-4.