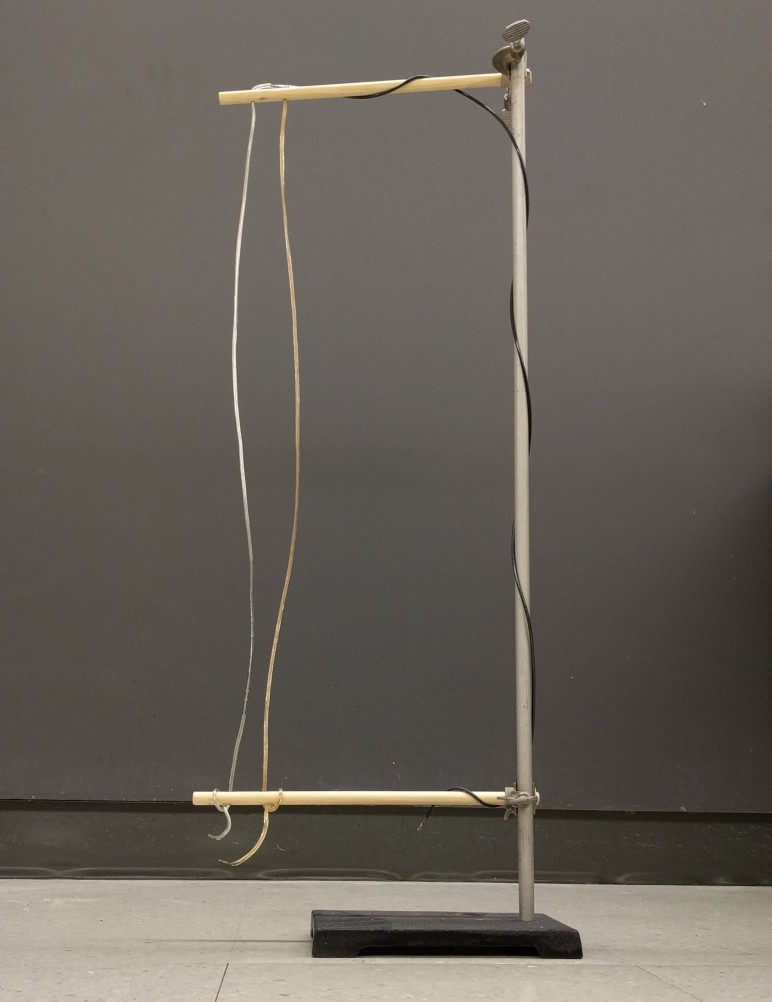
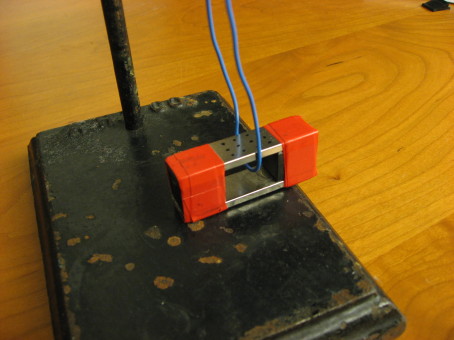
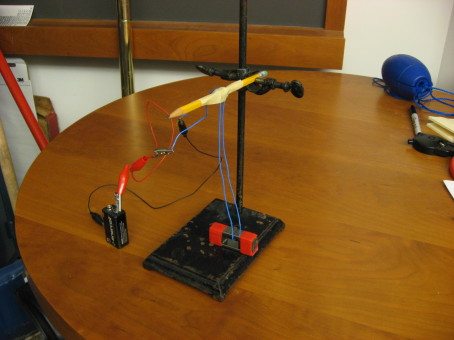
High current from the jump starter makes the wires jump together or apart, depending on how the circuit is wired. Connections are set up so that the clamps can be attached to the bottoms of the two lamp wires for antiparallel currents (series) or so that one clamp can be connected to the black-coated third wire and the other to the two lamp wires together for parallel currents.
Make sure not to leave the current on for very long, as the wires will get hot enough to melt the insulation. The instructions for the jump starter say to leave it plugged in when it’s not in use.
Location: L01, section B2