Skip to content
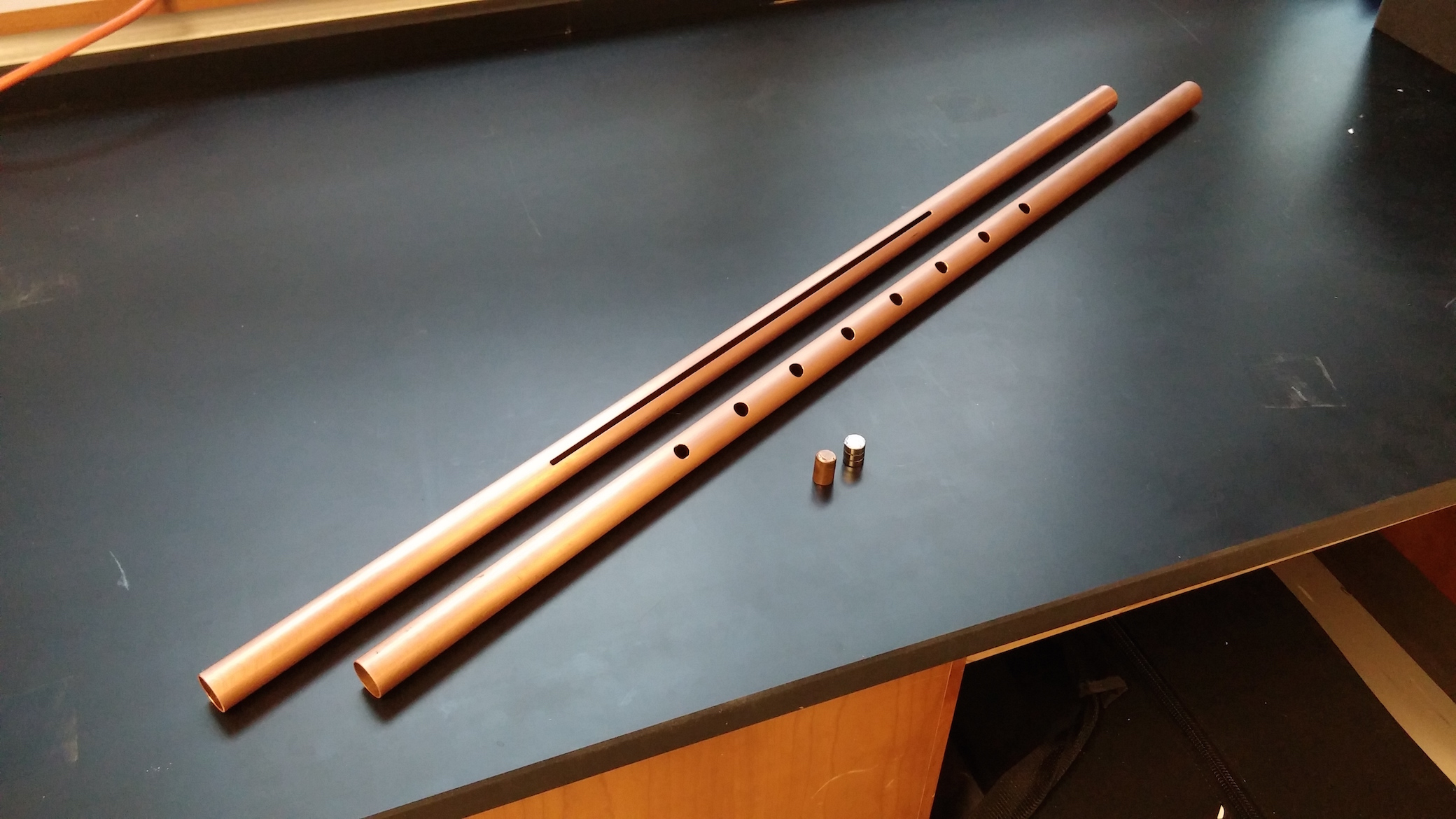


- Use Lenz’s law to explain extremely slow descent of neodymium
magnet through copper pipe.
- Hold pipe in a vertical orientation; drop magnet through
top opening of pipe; watch descent through holes in pipe.
- Try pipe with continuous slit to see difference in effect.
- Use copper slug to show speed of descent of non magnetic object.
Location
- Pipes located in L01, right-hand side between A2 and B1.
- Magnet in L01, section B2.


- Use principles of electromagnetic induction and Lenz’s Law
to explain why magnet rolls so slowly down metal incline.
- Located in L01, section B2.
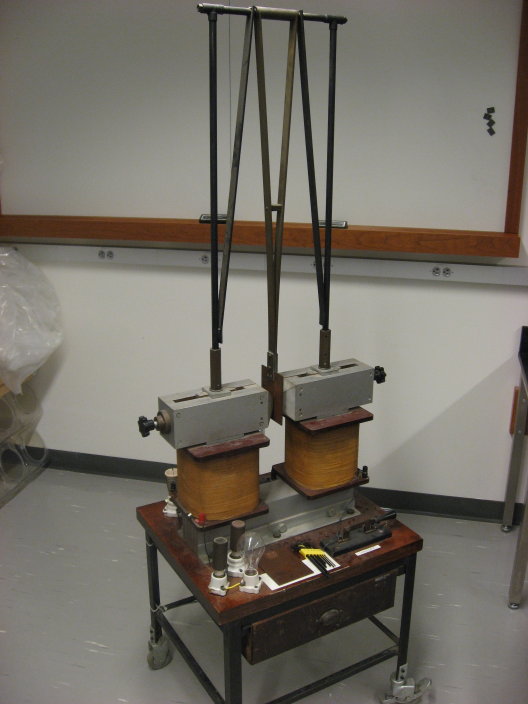


- Purpose: Demonstrate the effect of eddy currents on motion of metal pendulum in strong B-field.
- Pendulum accessories include two interchangeable copper plates, one of which is serrated. Serrated copper plate experiences little resistance to motion through magnetic field.
- Located in L03


- Use Lenz’s Law (and Faraday’s Law) to explain why aluminum plate (non-magnetic) resists motion through magnetic field.
- Located in L01, section B2.
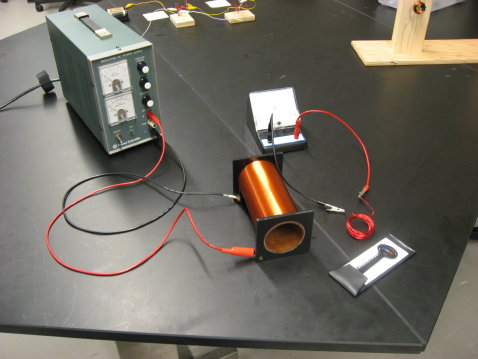

- Purpose: Illustrate principles of electro-magnetic induction.
- Send current through solenoid and measure direction of B-field
using B-field indicator (magnaprobe). Place coil of wire in front of solenoid
and quickly adjust current; galvanometer will indicate induced emf consistent
with Lenz’s law.
Location
- Solenoid and wire coil located in L01, section B2.
- Power supply- L35, section F1;
- magnaprobe- L35, section E4, top shelf
- galvanometers- L35, section F3









