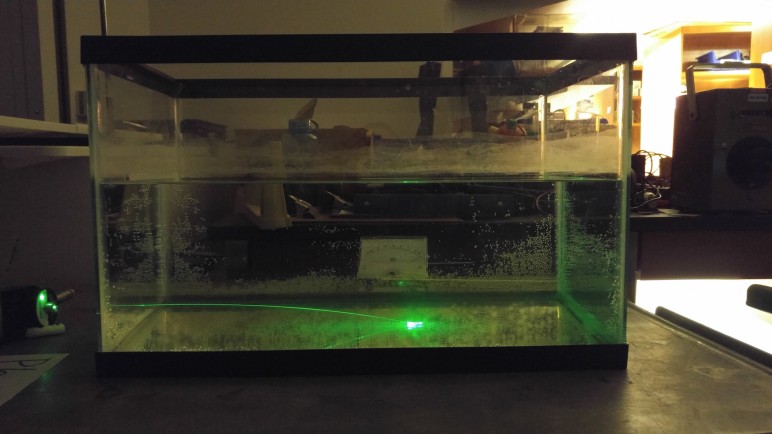
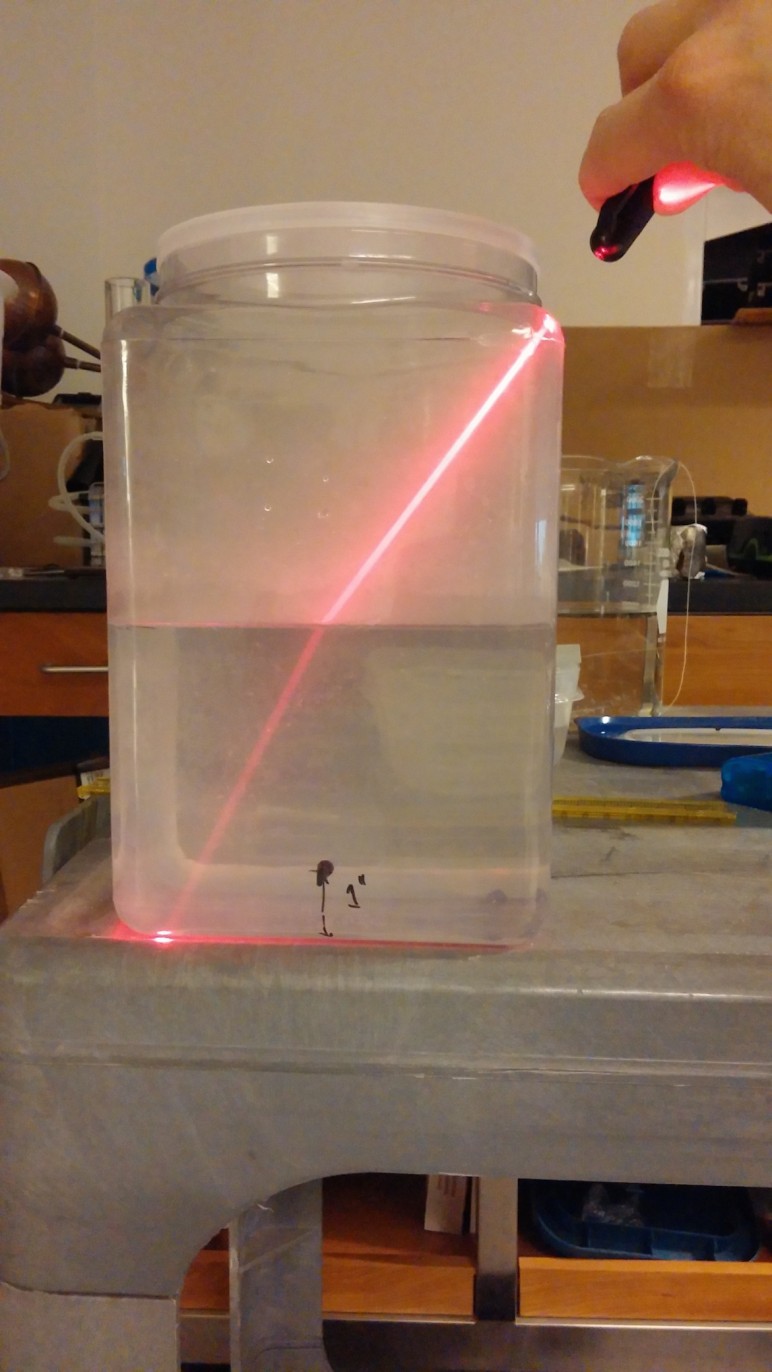
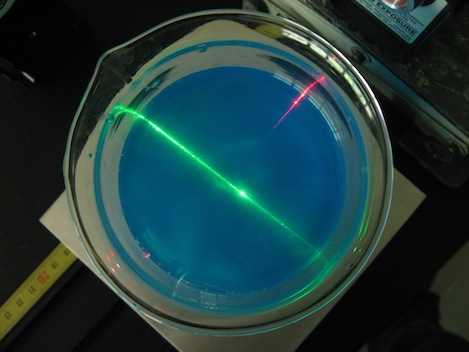
- Tank shown above contains a solution of sugar water that becomes more and more concentrated with depth. As sugar water has a higher index of refraction than pure water, the sugar density gradient produces a depth-dependent index of refraction. A laser beam shot through the solution, initially parallel to the bottom of the tank, will bend downward and hit the bottom.
- To prepare solution: pour sugar into empty tank, a few centimeters thick. Then, using a hose, very slowly (so as not to agitate sugar) fill the tank with water about halfway full.
- Tank located in L01, section B6. Sugar in L35, under sink. Laser in L35, section A5.