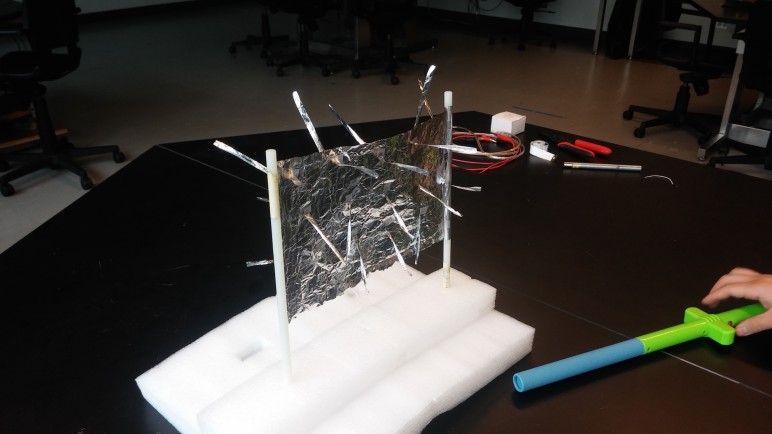
Use “Fun Fly Stick” to charge up conductive sheet.
Mylar strands align with electric field.
Place support rods together to form cylinder. Electric field of cylinder points outward radially.
- Located in L01, section A-2
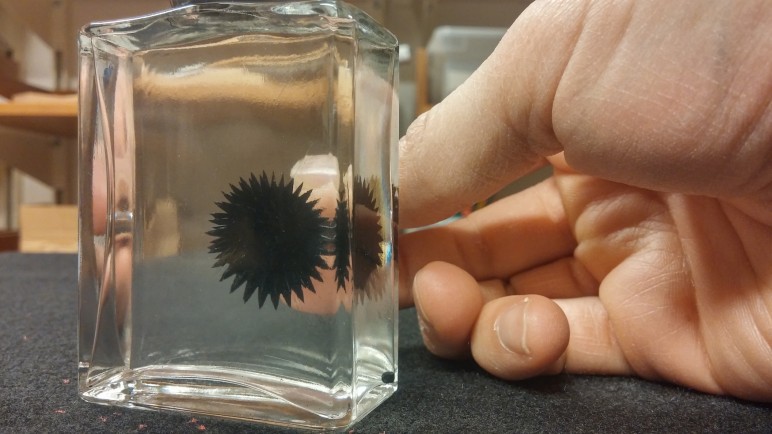

Developed by NASA Scientist Steve Papell in the 1960’s, Ferrofluid is a colloidal liquid made of paramagnetic nano particles. When subjected to a magnetic field, the nanoparticles form regular patterns of peaks and valleys.
For an interesting list of modern applications see:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ferrofluid


Notes about use









Location






Some ideas for experiments beyond the typical shock-myself-and-my-students: